Welcome to our first Webinar of 2024 in which we are happy to host Dr. Carol Esson.
In this talk today, Carol will be presenting the key questions and outcomes of her PhD research project on Snow Leopards in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia.
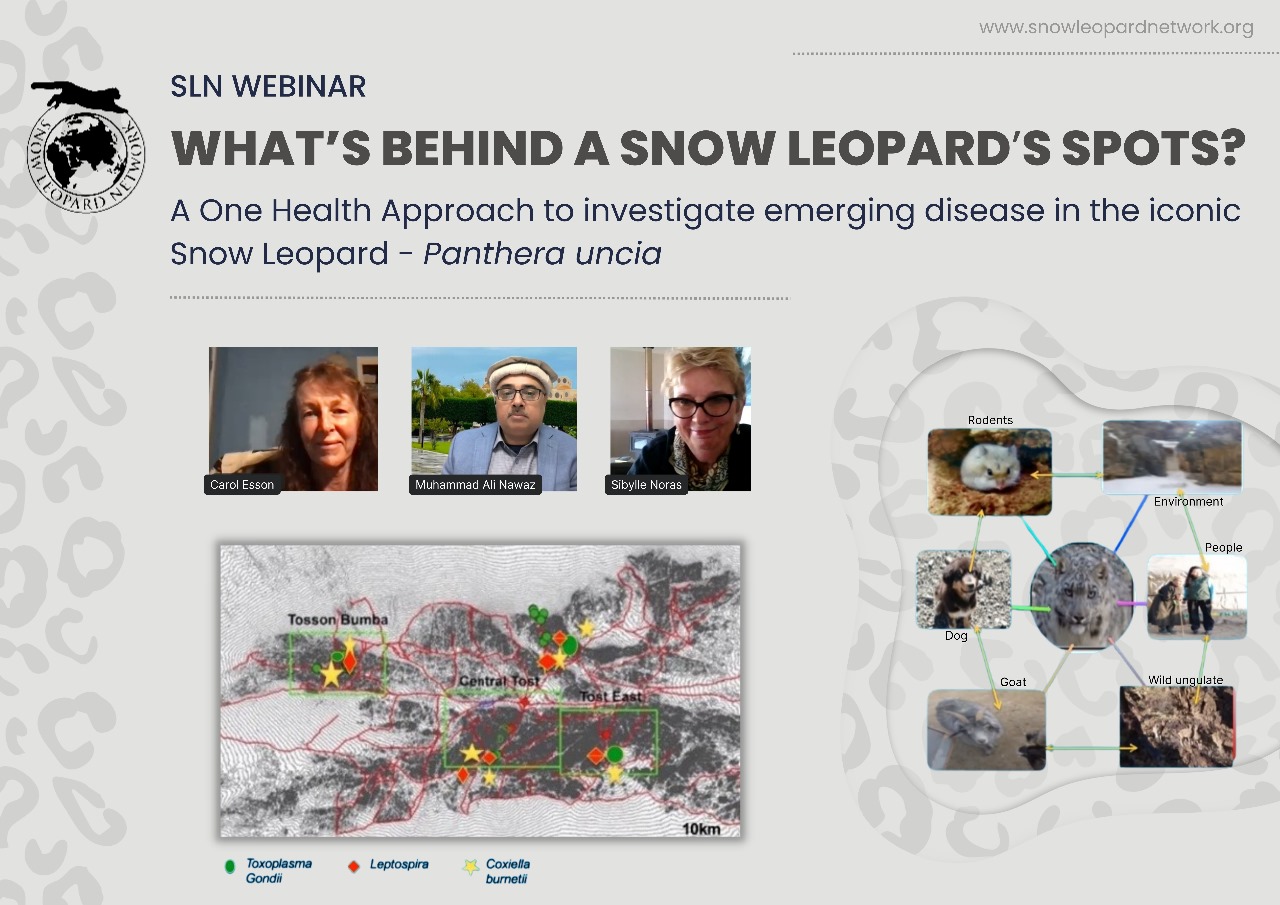
Emerging wildlife diseases are a growing concern across the world. They have wide-spread and diverse ramifications, including effects on and interactions between, endangered species, production animals, human health and livelihoods (Smith et al. 2009). In the future, successful disease control will have to reach across the traditional boundaries of conservation, human health and production animal diseases to achieve integrated disease assessment and control programs.
A One Health Approach was utilised to investigate disease threats to an endangered species in a remote location. Carol will talk about the rationale behind the research project design, the techniques used, the analysis and outcomes and how the results should lead to an improved understanding of how we can manage these populations from any future disease threats. These techniques we employ will be able to be extrapolated to other threatened species in remote locations.