We are delighted to invite you to join us for this special webinar presentation with Rodney Jackson and Rinzin Phunjok Lama.

About the Talk:
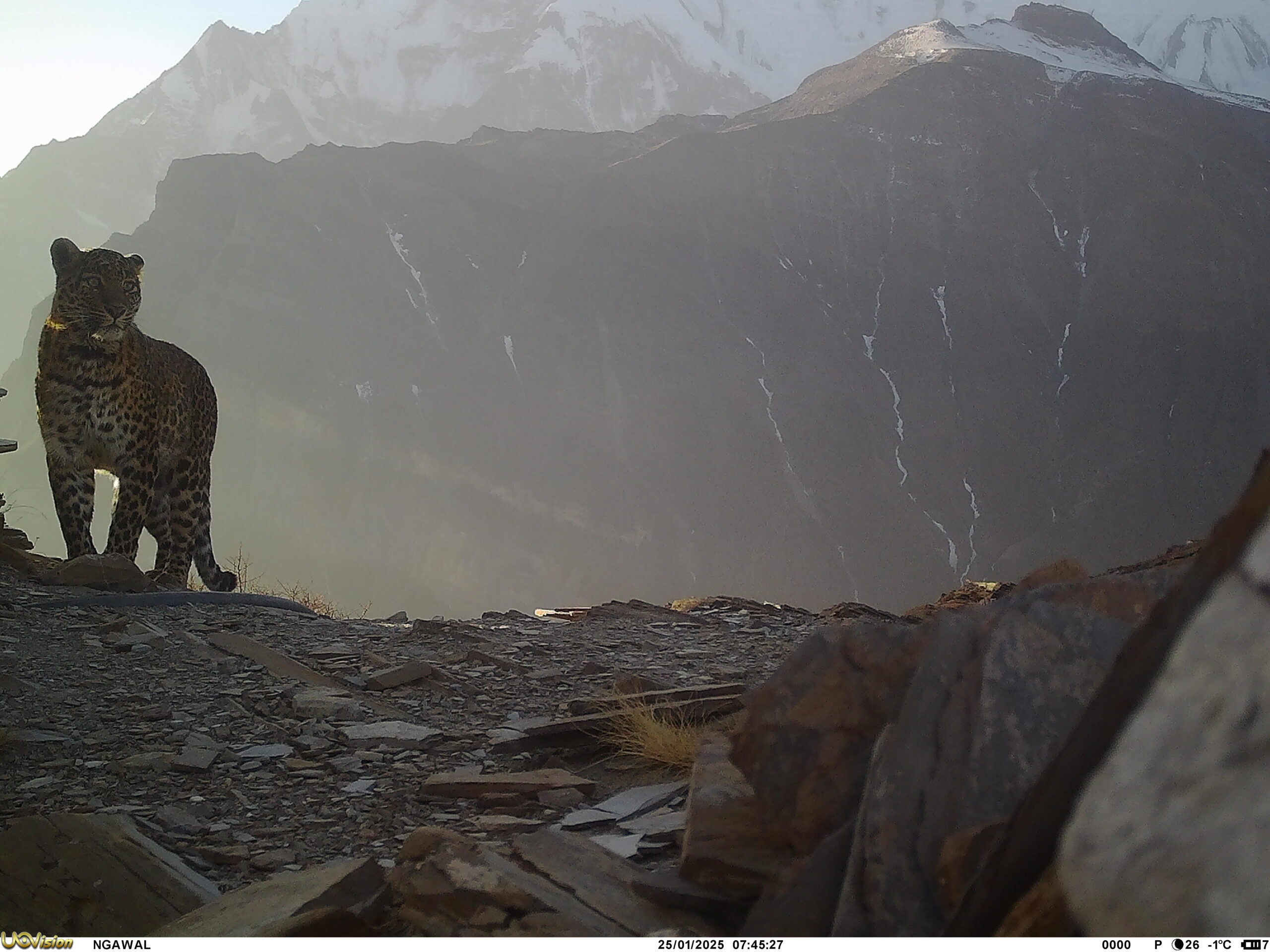
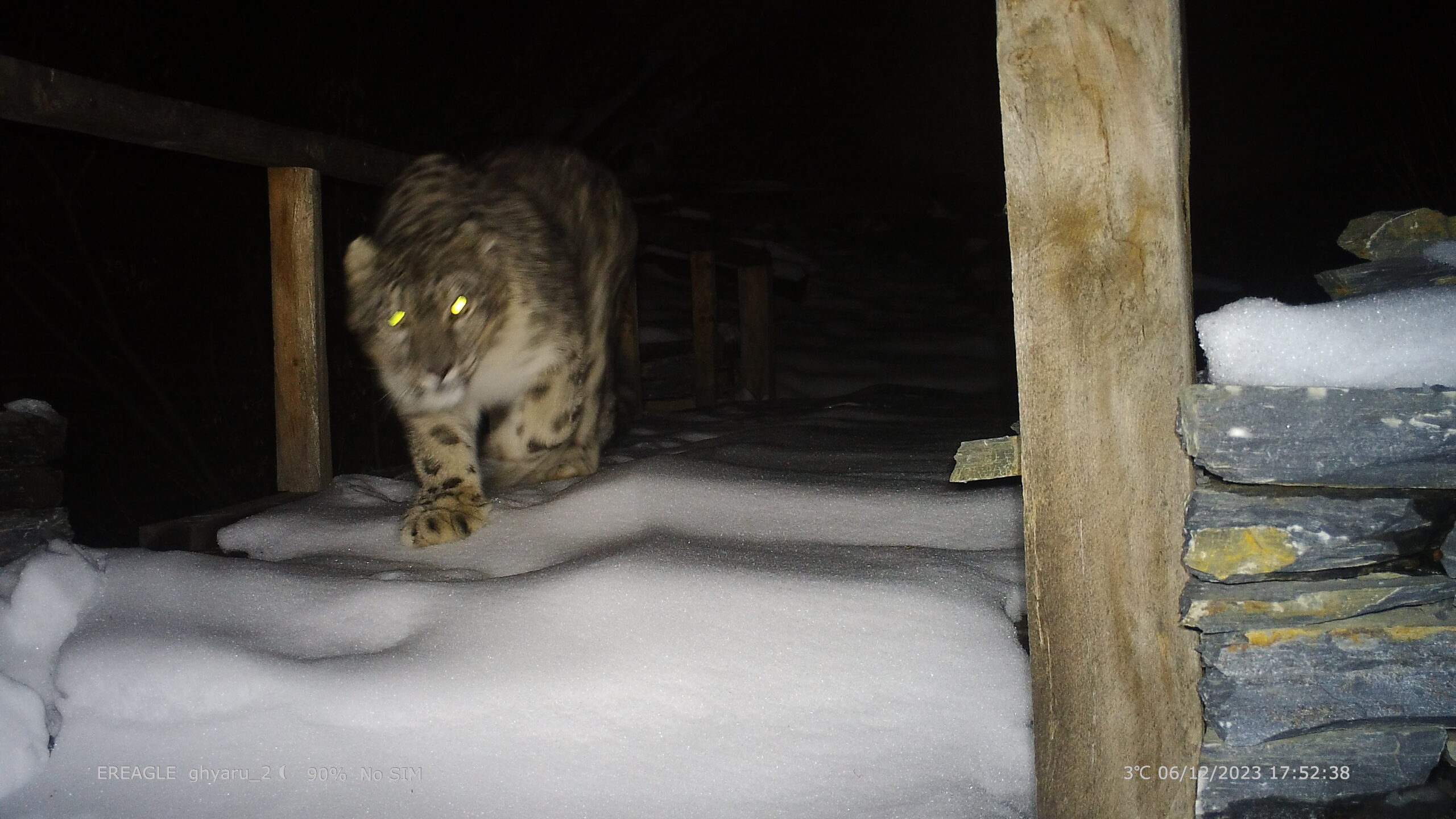
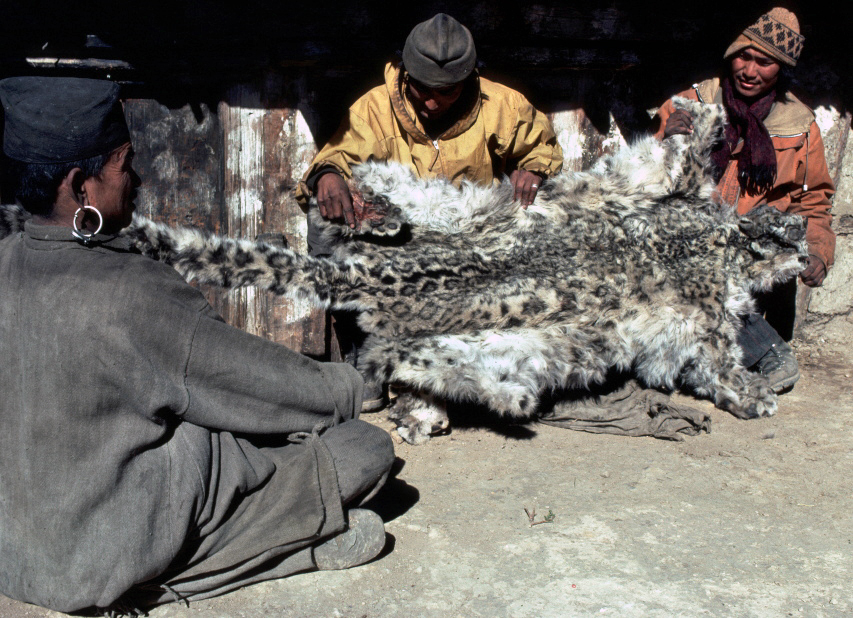
In this webinar, Rodney Jackson – the first scientist to radio-collar snow leopards, will share milestones along his 45+year career dedicated to the research and conservation of this seldom seen big cat. Much of Rodney’s pioneering work was undertaken before the introduction of PC computers, hand-held GPS devices, or smart phones and without benefit of walkie-talkies or digital cameras. His study area in Western Nepal was only reachable via a 12-day or more trek over arduous, dangerous trails, with all supplies, food and equipment for the 3–6-month field session portered in by local people or more rarely on yaks. Rodney and his team rarely saw snow leopards but nevertheless were able to gather extensive information on snow leopard behavior, movements and habitat selection using telemetry and tracking social sign-posts along travel lanes favored by male and female snow leopards alike.
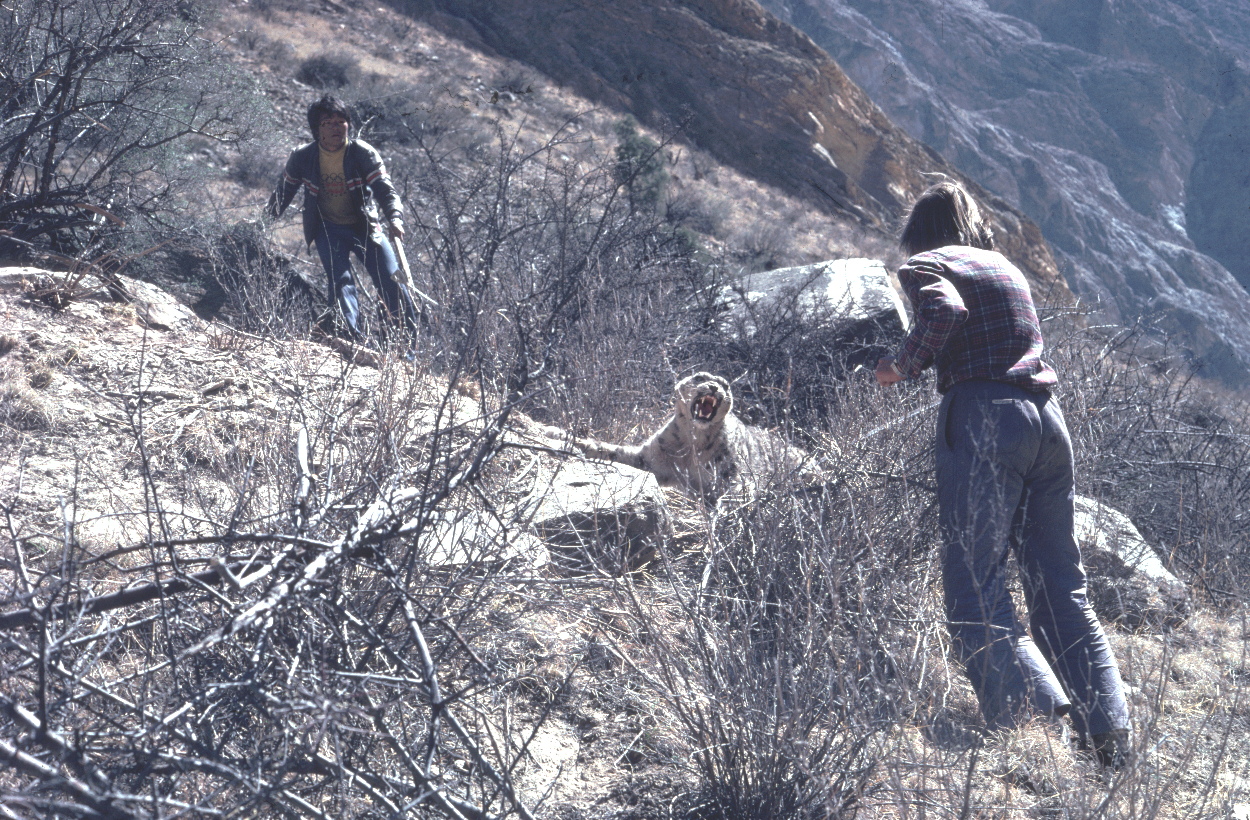

From this seminal study, Rodney will share his work training Protected Area rangers in Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Mongolia using sign transects (SLIMS) to conducting the first camera trap and non-invasive studies, pioneering community-driven conservation and wildlife-livestock conflict mitigation to working with Traditional Cultural Elders, shamans and educators in Central Asia. Over the past few decades, he has focused on mentoring the next generation of conservationists.
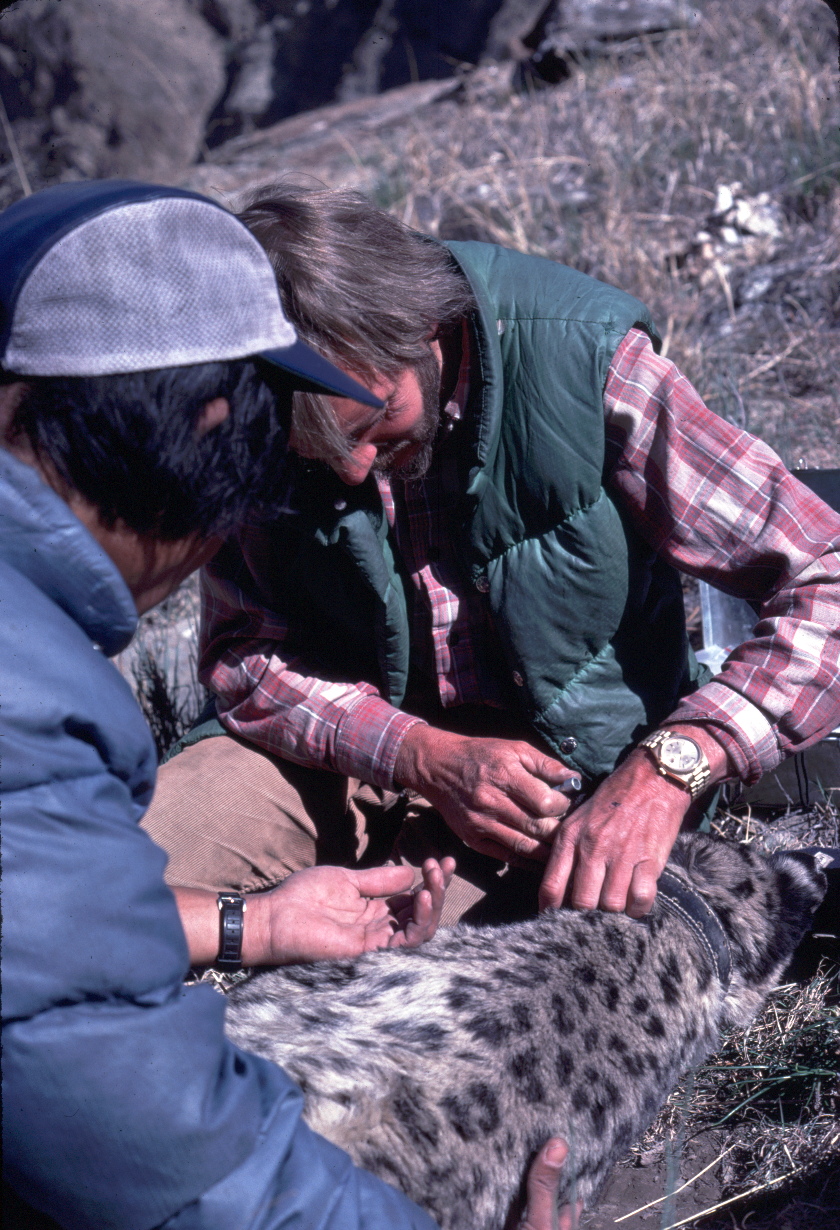

Rodney and Rinzin will then discuss how studies of snow leopards and their prey have changed from the “muddy boots” days of the 1970s-1990’s to involve closer and more interactive exchanges with local communities for resolving human-wildlife conflict, address climate change and laying basic framework for empowering local people to become increasingly effective as citizen scientists and front-line guardians of the snow leopard, its mountain biodiversity and their own environment. While key questions remain, like “how many snow leopards are there?”, the need for more strategic conservation action to address many growing threats remains. Indeed, the future of snow leopards’ rests with the current generation of biologists, ecologists and social scientists — men and women working in tandem with local people (especially pastoralists and herders) and government rather than being heavily driven by academia.
About our Speaker:
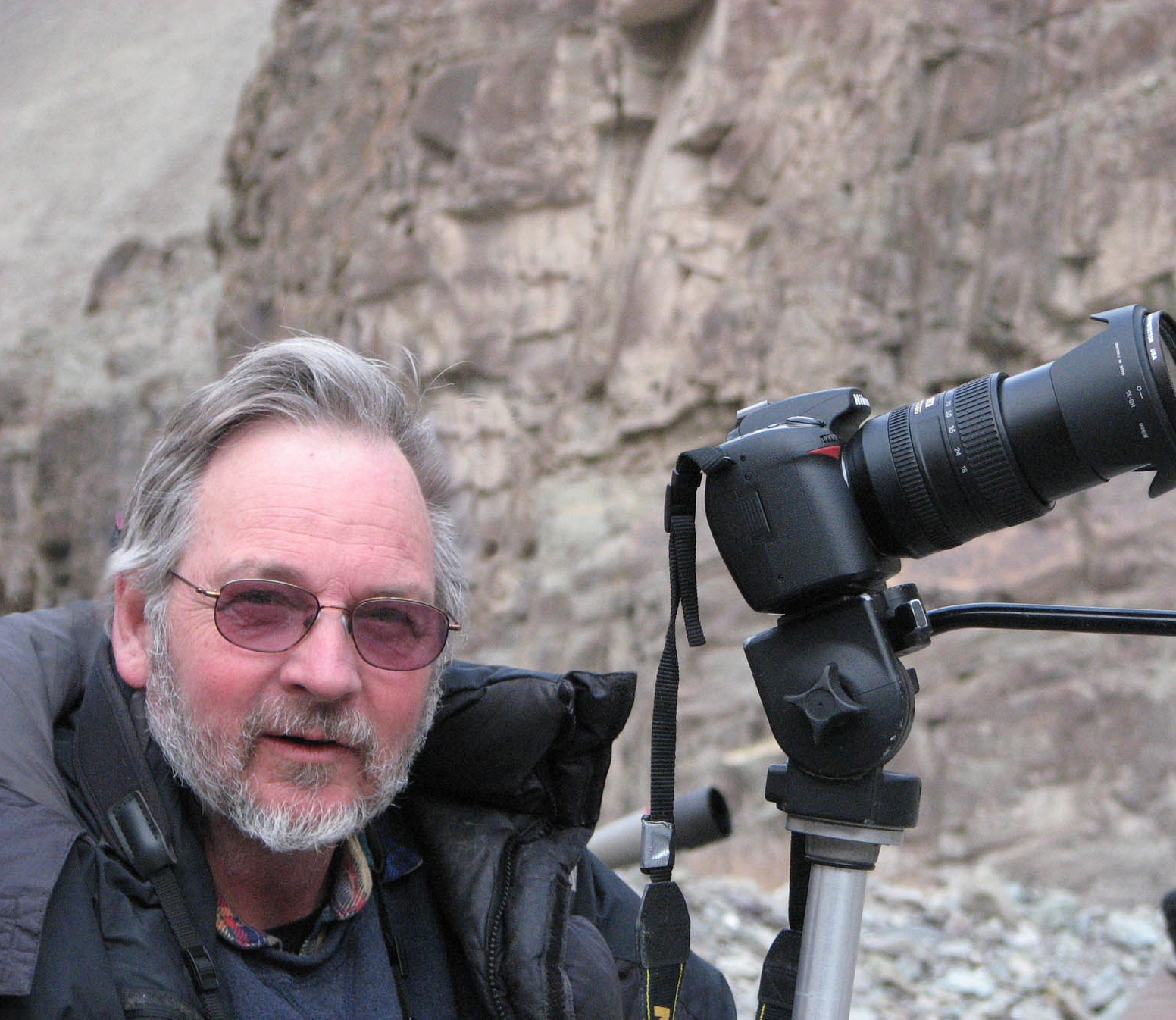

Dr. Rodney Jackson was born in South Africa and grew up in Southern Rhodesia, now Zimbabwe. In 1968 he came to the US to obtain his master’s degree from UC Berkeley, and upon graduating he started his career as an independent wildlife and land management consultant in California and eastern Africa. In 1981 he received the Rolex Award for Enterprise that enabled his pioneering radio-tracking study of snow leopards in the remote mountains of the Nepalese Himalaya. This four-year study led to a National Geographic cover story in 1986 and his PhD in 1996 from the University of London.
Rodney is widely acknowledged as a leading world expert on snow leopards and their high-mountain ecosystem. A founder member of the International Snow leopard Trust, in 2000 he and his wife Darla Hillard launched the Snow Leopard Project which evolved into the Snow Leopard Conservancy (SLC) based on his 40+ years’ experience gained in working closely with rural herders and farmers whose lives are directly impacted when snow leopards’ prey upon their livestock. In 2003 Rodney and Darla established the SLC – India Trust, now an independent NGO based in Ladakh, India.
Rodney prepared the original snow leopard section for the IUCN-World Conservation Union’s Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan for Cats published in 1996. He is a long-time member of IUCN’s Cat Specialist Core Group and served on the Snow Leopard Network Steering Committee between 2003 and 2008. Rodney led the standardization of snow leopard field survey methods across the twelve snow leopard host countries, known as the Snow Leopard Information Management System (SLIMS). Working with partner agencies, he has trained biologists in survey and conservation methods for parks and nature reserves in China, Pakistan, Mongolia, Nepal, Bhutan, and India. SLIMS has since been superseded by advancements in camera trapping and genetic technology for surveying snow leopard populations. Rodney has served as a consultant to the World Bank on a GEF protected areas project in Pakistan, and to the UNDP for a GEF Biodiversity Conservation Project in Upper Mustang Project in Nepal. He assisted ACTED, to develop community-based wildlife initiatives in Tajikistan centered around snow leopards and Marco Polo sheep, funded by UNESCO, along with providing technical support for transboundary and wildlife management for the Makalu-Barun National Park (Nepal)i, the Qomolangma National Nature Preserve (Tibet, China) and four protected areas in Pakistan.
Rodney has contributed to numerous scientific peer-reviewed papers and general interest publications targeting administrators and the general public. He is an Honorary Fellow of the California Academy of Sciences and a five-time finalist for the Indianapolis Prize, among the world’s most prestigious and largest individual award for animal conservation. He numerous presentations have reached audiences across America to Britain, South Africa, Australia and Nepal.
Rodney retired as SLC’s Executive Director in 2022, although currently serving as President of its Board of Directors, while also devoting his time mentoring the next generation of promising range-country conservationists and of course keeping his hand in special projects (including using drones for enumerate prey species in Mongolia).

About our Facilitator:
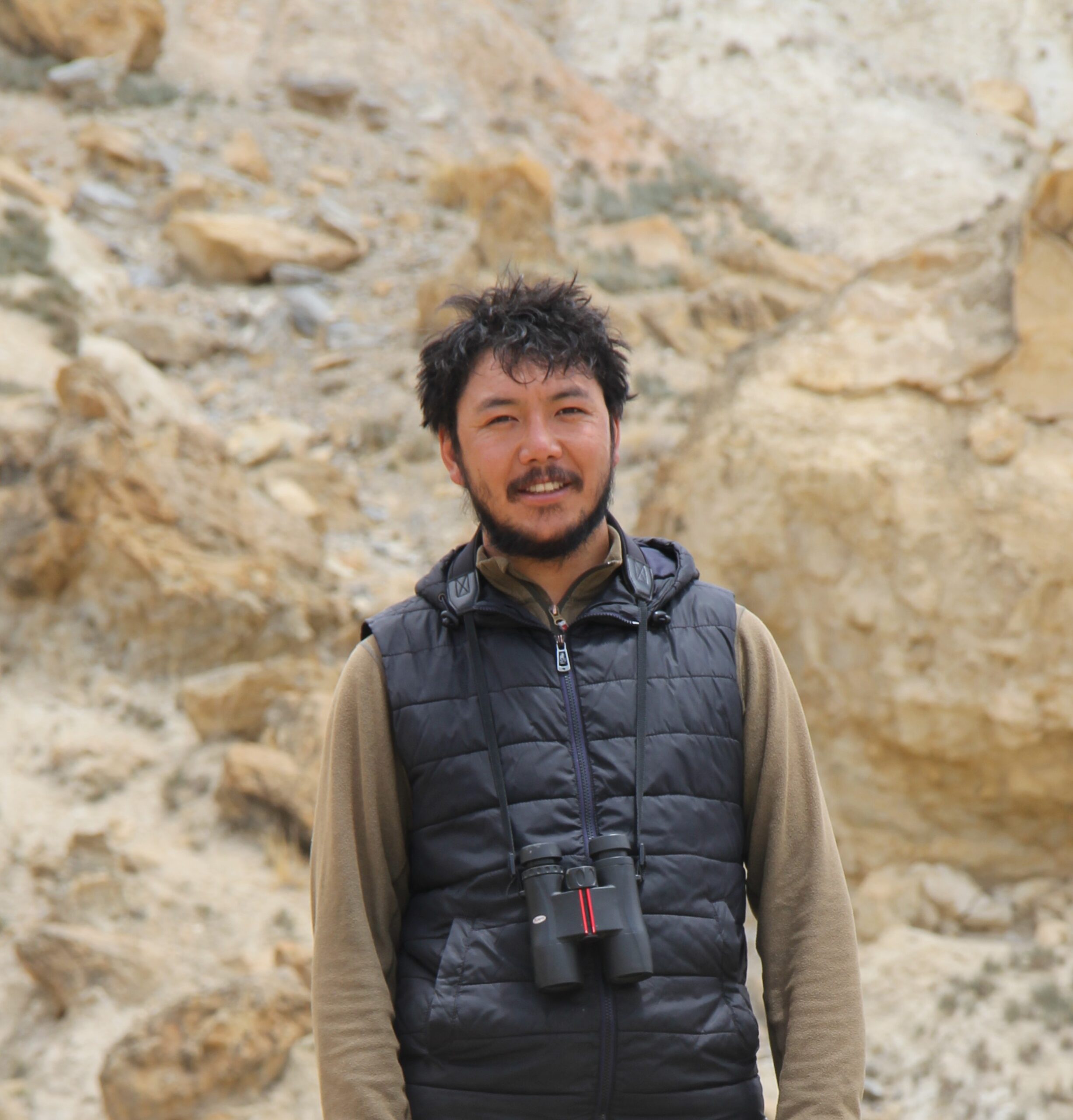

Rinzin Phunjok Lama is an internationally recognized conservationist from Humla, Nepal. He holds a BSc in Forestry from Tribhuvan University, Institute of Forestry, Pokhara, and a Master’s degree in International Nature Conservation jointly from the University of Göttingen, Germany, and Lincoln University, New Zealand. Rinzin currently leads UKALI, a community-led initiative focused on trans-Himalayan biodiversity conservation in Nepal, with emphasis on his native Upper Karnali region.
Since 2014, Rinzin has been actively involved in high-altitude wildlife research and conservation, contributing numerous peer-reviewed publications. His leadership and dedication have earned him several prestigious accolades, including the WWF Nepal Conservation Award (2020), the prestigious Rolex Award for Enterprise (2021), and recognition as one of Time magazine’s Next Generation Leaders (2022). In 2024, he received the Future for Nature Award and the National Geographic Wayfinder Award, and was named among OnlineKhabar’s “40 Under 40” most influential youths in Nepal.)
Date/Time:
Thursday, 10th July at 09:15 AM (Bishkek time)
Location:
ZOOM, to join this talk, REGISTER HERE
Please note:
- If you have never used Zoom before, we recommend that you try the link 10 minutes before the start of the lecture.
- Please feel free to write questions in the comment area and there will be time for questions/discussion at the end of the talk.
- Please note that the session will be recorded and later featured on the SLN website. If you have concerns about this please let us know before the session










 (Photos by Ben Buckland)
(Photos by Ben Buckland)
 (Photos by Ben Buckland)
(Photos by Ben Buckland) (Photos by Ben Buckland)
(Photos by Ben Buckland)
 (Photos by Ben Buckland)
(Photos by Ben Buckland)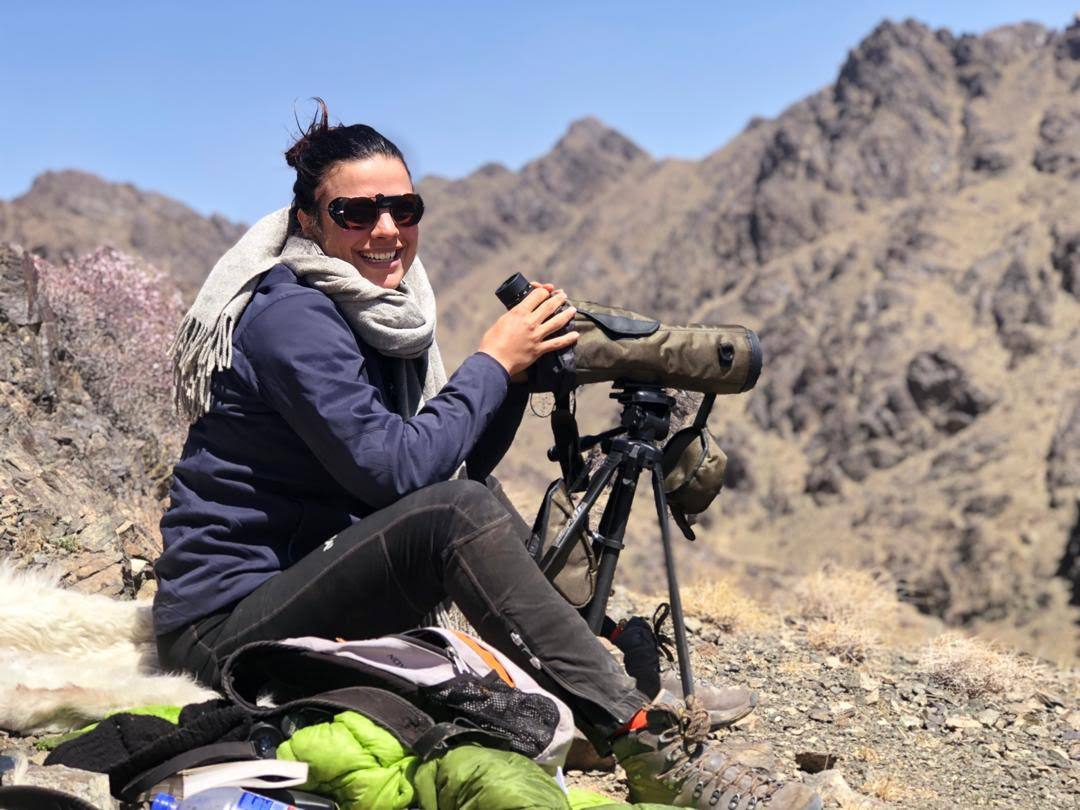
 (Photos by Ben Buckland)
(Photos by Ben Buckland)














